Remote Debug a Pod’s Java Process
Simple steps for remote debugging a Java process running on a k8 pod:
-
Edit deployment and add the following parameters to the Java start line:
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=127.0.0.1:5005Also add the following port mapping at the section
container → portsin the deployment:- containerPort: 5005 protocol: TCP -
Safe, wait for the new pods and then add a port forward for port 5005 for this pod:
kubectl port-forward podname 5005 -
Now add a new run configuration in IntelliJ
Edit Configurations → Add New Configuration → Remote JVM Debug -
Set breakpoints, happy debugging! :)
Simple One-Class HTTP Server for Testing Purpose
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpExchange;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class HttpServe {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpServer server = HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress(9000), 0);
server.createContext("/", new CustomHandler());
server.setExecutor(null);
server.start();
}
static class CustomHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange t) throws IOException {
String response = String.format("Now it is %s", ZonedDateTime.now());
t.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = t.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
}Copy & Paste on a remote system with one click:
cat << EOF > HttpServe.java && javac HttpServe.java && java HttpServe
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpExchange;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler;
import com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class HttpServe {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpServer server = HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress(9000), 0);
server.createContext("/", new CustomHandler());
server.setExecutor(null);
server.start();
}
static class CustomHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange t) throws IOException {
String response = String.format("Now it is %s", ZonedDateTime.now());
t.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = t.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
}
EOFCalling the service:
$ curl -s localhost:9000
Now it is 2022-10-27T08:09:46.387727300+02:00[Europe/Berlin]
Since Java 18 there is a webserver included, jwebserver: more information
|
Print Diagnostic RAM, CPU Information
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.MemoryMXBean;
import java.lang.management.ThreadInfo;
import java.lang.management.ThreadMXBean;
private static void logResourceUsage() {
MemoryMXBean memoryMXBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
var cpuInfos = new StringBuilder();
for (Long threadID : threadMXBean.getAllThreadIds()) {
ThreadInfo info = threadMXBean.getThreadInfo(threadID);
var cpuInfo = String.format("""
---
Thread name: %s
Thread State: %s
CPU time: %s ns
""",
info.getThreadName(),
info.getThreadState(),
threadMXBean.getThreadCpuTime(threadID)
);
cpuInfos.append(cpuInfo);
}
var info = String.format("""
=================================================
Initial memory: %.2f GB
Used heap memory: %.2f GB
Max heap memory: %.2f GB
Committed memory: %.2f GB
Thread-Infos:
%s
=================================================
""",
((double) memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getInit() / 1073741824),
((double) memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getUsed() / 1073741824),
((double) memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getMax() / 1073741824),
((double) memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getCommitted() / 1073741824),
cpuInfos
);
System.out.println(info);
}Show processes
jpsCreate heap dump from running process
jmap -dump:format=b,file=/tmp/heap.bin 2381Create jhat webserver to show heap dump analysis
jhat -port 7401 -J-Xmx4G heap.binCaller / Calling class from Stacktrace
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
String className = stackTrace[2].getClassName();Print Thread Dump with Deadlock Analysis
jcmd PID Thread.printRecompile Class and Set Method Return to true
-
Download Recaf from GitHub: https://github.com/Col-E/Recaf
-
Open Jar file in Recaf
-
Find the designated class and method
-
Right-click on the method and select
Opcodes -
Select the last line with opcode
IRETURN -
Select
New Opcode before.. -
Select
Insnin the first dropdown andICONST_1as opcode from the second dropdown and click onAdd opcode -
Save the modified Jar-file (File – Save) and enjoy
Set Timezone in Unit Test
@Before
public void setup(){
TimeZone.setDefault(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
}Starting Java with Debugging enabled
java -Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,address=8000,server=y,suspend=y -jar target/vertx-websocket-chat-1.0.0-fat.jarDebugging with jdb
Connecting
jdb -attach localhost:8000 -sourcepath /project/hascode-sample/src/main/javaSet breakpoint
stop in com.hascode.sample.Example.doSth(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)Breakpoint hit
Outputs the thread-name (e.g. “thread=http-nio-8080-exec-1″), class-name, method-name, line-number and bci-counz (byte-code-instructions)
Exploring code at breakpoint
http-nio-8080-exec-1[1] listExploring data at breakpoint
---
http-nio-8080-exec-1[1] localshttp-nio-8080-exec-10[1] print VARIABLE ---
Add JUnit5 dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>JUnit BeforeAll without static
The test class must be configured not to use TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_METHOD which is the default, but TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS:
package com.hascode.tutorial;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInstance;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)
class MySpecialTest {
String authToken;
@BeforeAll
void setup(){
authToken = fetchAuthtoken();
}
@Test
void mustDoSomething(){}
}JUnit Parameterized Test with CSV Source
package com.hascode.tutorial;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.CsvSource;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class SampleParameterizedTest {
@ParameterizedTest(name = "[{index}] User with name <{0}> should be <{1}> years old")
@CsvSource({"Tim,22","Sally,43","Tina,19","Fred,84"})
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
void userNameAndAgeMustMatch(String userName, int age) {
var user = fetchUser(userName);
assertThat(user.age()).isEqualTo(age);
assertThat(user.name()).isEqualTo(name);
}
}The same example with a nice, more tabellaric view using pipes as delimiter string:
@ParameterizedTest(name = "[{index}] User with name <{0}> should be <{1}> years old")
@CsvSource(delimiterString = "|", textBlock = """
Tim | 22
Sally | 43
Tina | 19
Fred | 84
""")
void userNameAndAgeMustMatch(String userName, int age) {
var user = fetchUser(userName);
assertThat(user.age()).isEqualTo(age);
assertThat(user.name()).isEqualTo(userName);
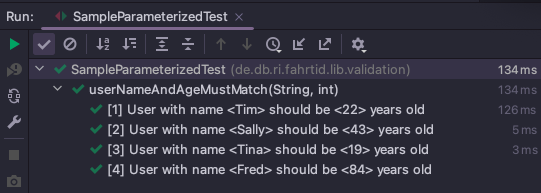
}Looks like this when ran in IntelliJ:
Add Failsafe Plugin
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>Use SLF4J and Logback with Maven
Maven dependencies:
<project>
<properties>
<logback.version>1.0.3</logback.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.6.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>Example logback.xml:
<configuration>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>Logstash Logback JSON Logging Configuration
| If log messages of logged exceptions are swallowed, it might be because the stacktraces are too long, the following configuration is helping! |
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="net.logstash.logback.encoder.LoggingEventCompositeJsonEncoder">
<providers>
<timestamp>
<fieldName>timestamp</fieldName>
<pattern>yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'</pattern>
<timeZone>UTC</timeZone>
</timestamp>
<logLevel/>
<threadName>
<fieldName>thread</fieldName>
</threadName>
<loggerName>
<fieldName>logger</fieldName>
</loggerName>
<message/>
<stackTrace>
<throwableConverter class="net.logstash.logback.stacktrace.ShortenedThrowableConverter">
<maxLength>256</maxLength>
<shortenedClassNameLength>20</shortenedClassNameLength>
<exclude>^sun\.reflect\..*\.invoke</exclude>
<exclude>^net\.sf\.cglib\.proxy\.MethodProxy\.invoke</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.InvocableHandlerMethod</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter\.invokeHandlerMethod</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter\.handle</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.DirectMethodHandleAccessor\.invoke</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.FrameworkServlet\.java</exclude>
<exclude>^org\.springframework\..*\.ApplicationFilterChain\.doFilter</exclude>
<exclude>^java\.lang\..*\.Method\.invoke</exclude>
</throwableConverter>
</stackTrace>
<contextName/>
<logstashMarkers/>
<arguments/>
</providers>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root>
<appender-ref ref="stdout"/>
</root>
</configuration>Get Class Information from Generic Class without Constructor Parameter
Class<T> entityClass = (Class) ((ParameterizedType) getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[0];Externalizable Example
package com.hascode.sample;
import java.io.Externalizable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class User implements Externalizable {
private String name;
private ZonedDateTime birthday;
public User(){}
public User(String name, ZonedDateTime birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public ZonedDateTime getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("User{");
sb.append("name='").append(name).append('\'');
sb.append(", birthday=").append(birthday);
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeObject(birthday);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.name = in.readUTF();
this.birthday = (ZonedDateTime) in.readObject();
}
}package com.hascode.sample;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
User user = new User("Fred", ZonedDateTime.now());
// serializing
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(
"user.ser"); ObjectOutputStream outStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fos)) {
System.out.printf("serializing user: %s\n", user);
outStream.writeObject(user);
}
// deserializing
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(
"user.ser"); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fis)) {
User user1 = (User) in.readObject();
System.out.printf("deserialized user: %s\n", user1);
}
}
}Writing a custom Classloader
package io.hascode.tutorial;
public class ClassLoadSample {
public static class MyCustomClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
protected MyCustomClassLoader() {
super(MyCustomClassLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("searching for class "+name);
return super.findClass(name);
}
}
static class SampleClass {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
var myloader = new MyCustomClassLoader();
try {
var clazz = myloader.loadClass("io.hascode.tutorial.ClassLoadSample$SampleClass");
System.out.println(clazz);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Lambda Expression implementing multiple Interfaces
Object r = (Runnable & Serializable) () -> {};CDI / Weld Logging for GlassFish
add to domaindir/config/logging.properties
org.jboss.weld.level=FINECreate full self-contained application image with jpackage
jpackage --type app-image -n name -p modulePath -m moduleName/classNamejpackage --type app-image -i inputDir -n name --main-class className --main-jar out.jarService Discovery using ServiceLoader
package com.hascode.api;
interface MyService {}package com.hascode.impl1;
class MyServiceImpl implements MyService {}package com.hascode.impl2;
class AnotherMyServiceImpl implements MyService {}ServiceLoader serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(MyService.class);
for (MyService s : serviceLoader) {
System.out.println(s);
}// SPI Mechanism to load from external jar-file
package com.someotherprovider;
class CustomMyServiceImpl implements MyService {}// create a file named com.hascode.api.MyService in META-INF/services with following content:
com.someotherprovider.CustomMyServiceImplDisassemble Java Class
javap -c Sample.classDebugging SSL/TLS Connection Problems
Add the following JVM start parameter
java -Djavax.net.debug=ssl:handshake:verboseor for more logging:
java -Djavax.net.debug=ssl:handshake:verbose:keymanager:trustmanager -Djava.security.debug=access:stackResources:
-
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/ReadDebug.html == Importing Certificates into the Keystore
View cert > Details > Save to file (format: Base 64 X.509 / .CER)
keytool -import -file /tmp/downloadedCert.cer -keystore /tmp/myKeystoreDefault password here is: changeit
Keystore passed as parameter to Maven:
mvn -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/tmp/myKeystoreList Certificates in Keystore
keytool -list -keystore /etc/ssl/certs/java/cacertsRead SSL Certificate Information from pem file
keytool -printcert -file certificate.pemDownload SSL Certificate from Host/Post
Supported since Java 9 ..
keytool -printcert -rfc -sslserver HOST:PORTLog4j 1.x log by package to different log files
Main class calling two classes in separate packages
package com.hascode.tutorial;
import com.hascode.tutorial.alpha.Foo;
import com.hascode.tutorial.beta.Bar;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String input = "hello, logger";
new Foo().doSth(input);
new Bar().doSth(input);
}
}Class in package com.hascode.tutorial.alpha
package com.hascode.tutorial.alpha;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Foo {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
public void doSth(String input) {
log.info("doSth called with parameter {}", input);
System.out.println("foo " + input);
}
}Class in package com.hascode.tutorial.beta
package com.hascode.tutorial.beta;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Bar {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
public void doSth(String input) {
log.info("doSth called with parameter {}", input);
System.out.println("bar " + input);
}
}Configuration file log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, CONSOLE
log4j.logger.com.hascode.tutorial.alpha=DEBUG, ALPHA
log4j.logger.com.hascode.tutorial.beta=DEBUG, BETA
log4j.appender.CONSOLE=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c:%L - %m%n
log4j.appender.ALPHA=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.ALPHA.File=./alpha.log
log4j.appender.ALPHA.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.ALPHA.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c:%L - %m%n
log4j.appender.BETA=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.BETA.File=./beta.log
log4j.appender.BETA.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.BETA.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c:%L - %m%nRunning the program writes to console and following log files:
alpha.log
2016-05-19 15:22:30 INFO com.hascode.tutorial.alpha.Foo:10 - doSth called with parameter hello, loggerbeta.log
2016-05-19 15:22:30 INFO com.hascode.tutorial.beta.Bar:10 - doSth called with parameter hello, loggerFull sources available here.
Java FX 2 Maven Dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>javafx</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<systemPath>${java.home}/lib/jfxrt.jar</systemPath>
<scope>system</scope>
</dependency>Java FX 2 Fullscreen Stage
@Override
public void start(final Stage stage) throws Exception {
Screen screen = Screen.getPrimary();
Rectangle2D bounds = screen.getVisualBounds();
stage.setX(bounds.getMinX());
stage.setY(bounds.getMinY());
stage.setWidth(bounds.getWidth());
stage.setHeight(bounds.getHeight());
[...]
}WildFly Deploy via Console
Deploy
jboss-cli.sh --connect --command="deploy target/myapp-1.0.0.war"Deployment Status
jboss-cli.sh --connect --command=deployment-infoUndeploy
jboss-cli.sh --connect --command="undeploy myapp-1.0.0.war"Patching WildFly
$ sh jboss-cli.sh
You are disconnected at the moment. Type 'connect' to connect to the server or 'help' for the list of supported commands.
[disconnected /] connect
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] patch apply ~/Downloads/wildfly-8.1.0.Final
wildfly-8.1.0.Final-weld-2.2.2.Final-patch.zip wildfly-8.1.0.Final.tar.gz
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] patch apply ~/Downloads/wildfly-8.1.0.Final-weld-2.2.2.Final-patch.zip
{
"outcome" : "success",
"response-headers" : {
"operation-requires-restart" : true,
"process-state" : "restart-required"
}
}Dynamic Proxy
package com.hascode.sample;
public interface SampleService {
String printInformation();
}package com.hascode.sample;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class SampleServiceInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return "test";
}
}package com.hascode.sample;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InvocationHandler handler = new SampleServiceInvocationHandler();
SampleService service = (SampleService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(SampleService.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{SampleService.class}, handler);
System.out.println(service.printInformation());
}
}Java Receiver Parameters
Available since Java 8 (link)
package com.hascode.tutorial;
public class Foo {
void foo(@SampleAnnotation1 Foo this) {
}
class Bar {
Bar(@SampleAnnotation2 Foo Foo.this) {
}
}
}Add Class Diagrams to the JavaDocs using Maven and GraphViz
Step 1: Install graphviz:
sudo apt-get install graphvizStep 2: Modify maven reports
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.10.3</version>
<configuration>
<doclet>org.umlgraph.doclet.UmlGraphDoc</doclet>
<docletArtifact>
<groupId>org.umlgraph</groupId>
<artifactId>doclet</artifactId>
<version>5.1</version>
</docletArtifact>
<show>private</show>
<additionalparam>-all -constructors</additionalparam>
<useStandardDocletOptions>false</useStandardDocletOptions>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>Step 3: Generate JavaDocs using Maven
mvn siteSeparating Unit and Integration Tests with JUnit Categories
Create a marker interface for the JUnit category:
package com.hascode;
public interface IntegrationTest {}
Write an integration test and annotate it with @Category using the marker interface as value
import com.hascode.IntegrationTest;
import org.junit.experimental.categories.Category;
@Category(IntegrationTest.class)
public class MyIntegrationTest {
// ...
}Now configuring the Maven Surefire Plugin (Unit-Tests) and the Failsafe Plugin (Integration-Tests)
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.19.1</version>
<configuration>
<excludedGroups>com.hascode.IntegrationTest</excludedGroups>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.19.1</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<groups>com.hascode.IntegrationTest</groups>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>Unit tests may be run now with mvn test, integration tests with mvn verify or mvn integration-test.
JAX-RS return a generic list in a Response
List<Book> list = new ArrayList<>();
GenericEntity<List<Book>> entity = new GenericEntity<List<Book>>(list) {};
Response response = Response.ok(entity).build();JAX-RS / Jersey – Return a JSON Array for a Collection with a single element
Lets say you’re mapping a collection of books e.g. List<Book> books using jaxb passed as a jaxrs Response .. you may encounter a situation where you receive the following JSON output if there are many books in the collection:
{
books:[
{id:1, title:"foo"},
{id:2, title:"bar"}
]
}But if there is only one book in the collection your receive a single JSON object instead of an array .. e.g.:
{
books:{
id:1, title:"foo"
}
}The solution is to provide a custom JAXBContext ContextResolver and advise the context always to render arrays here:
import javax.ws.rs.ext.ContextResolver;
import javax.ws.rs.ext.Provider;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import com.sun.jersey.api.json.JSONConfiguration;
import com.sun.jersey.api.json.JSONJAXBContext;
import com.hascode.entity.Book;
@Provider
public class BookContextResolver implements ContextResolver<JAXBContext> {
private final JAXBContext context;
private final Class[] types = { Book.class };
public PersonContextResolver() throws Exception {
this.context = new JSONJAXBContext(JSONConfiguration.mapped().arrays("books").build(), Book.class);
}
@Override
public JAXBContext getContext(final Class<?> objectType) {
for (Class type : types) {
if (type == objectType) {
return context;
}
}
return null;
}
}Increase Eclipse Memory Settings
In the eclipse/configuration directory edit the config.ini
--launcher.XXMaxPermSize
128M
-Xms1024m
-Xmx2048m
-XX:MaxPermSize=1048mDifferent Logging Library Placeholders
SLF4J
log.info("{}, {}", "Hello", "World");JULI Logger
log.log(Level.INFO, "{0}, {1}", new Object[]{"Hello", "World"});Seam Logger
log.info("#0, #1", "Hello", "World");Create heap dump on OutOfMemoryError
-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/path/to/save/dumpsJava Bean Validation add custom Validation Cases and Messages
Use the javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext to override the default validation error message.
|
Given is a simple bean validator for NIO Path objects:
package com.hascode.example;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
@Target({FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = PathIsAccessibleValidator.class)
@Documented
public @interface PathIsAccessible {
String message() default "PathIsAccessible"; (1)
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}And this the designated validator for our annotation marked fields:
public class PathIsAccessibleValidator implements ConstraintValidator<PathIsAccessible, Path> {
@Override
public boolean isValid(Path path, ConstraintValidatorContext ctx) {
ctx.disableDefaultConstraintViolation(); (2)
if (path == null) {
ctx.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate("{PathIsAccessible.IsNull}") (3)
.addConstraintViolation();
return false;
}
if (!path.toFile().exists()) {
ctx.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate("{PathIsAccessible.NonExistent}") (4)
.addConstraintViolation();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}| 1 | this is the default validation error message |
| 2 | we’re deactivating the default error message here |
| 3 | we’re setting a more specific error message |
| 4 | we’re setting another more specific error message |
Initialize XMLGregorianCalendar by lexical string representation
e.g. when using ugly legacy SOAP APIs.
XMLGregorianCalendar calendar = DatatypeFactory.newInstance().newXMLGregorianCalendar("2022-12-24T13:56:00.000+01:00");Java HTTP Proxy Configuration
Proxy configuration is done by setting the following JVM parameters:
- http.proxyHost
-
Proxy server host used for HTTP
- http.proxyPort
-
Proxy server port used for HTTP
- https.proxyHost
-
Proxy server host used for HTTPS
- https.proxyPort
-
Proxy server port used for HTTPS
- httpNonProxyHosts
-
List of proxy excemptions, separated by a pipe '|'
- http.proxyUser
-
User for proxy authentication
- http.proxyPassword
-
Password for proxy authentication
So a sample Java invocation with proxy settings added, might look like this one:
java -Dhttp.proxyHost=myproxyhost.io -Dhttp.proxyPort=8080 -Dhttps.proxyHost=myproxyhost.io -Dhttps.proxyPort=8080 -DhttpNonProxyHosts=127.0.0.1|localhost|169.254.169.254|amazonaws.comCreate Docker Image for Java Web App
FROM openjdk:17-jdk-alpine
RUN mkdir -p /usr/opt/my-app
COPY target/*.jar /usr/opt/my-app/my-app.jar
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT exec java -jar /usr/opt/my-app/my-app.jarCreate the image
docker build -t my-app:1.0 .Or a simple container with Java 17 based on alpine linux:
kubectl run java-pod --rm -it --image=openjdk:17-jdk-alpine -- shMock MeterRegistry in JUnit Test
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Metrics;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.simple.SimpleMeterRegistry;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
meterRegistry = new SimpleMeterRegistry();
Metrics.globalRegistry.add(meterRegistry);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
meterRegistry.clear();
Metrics.globalRegistry.clear();
}Generate JMeter Test from OpenAPI Spec with openapi-generator-cli and Docker
docker run --rm -v "${PWD}:/local" openapitools/openapi-generator-cli generate \
-i /local/myspec-1.2.3.yaml \
-g jmeter \
-o /local/jmeter